
With the development of multimodal large models and the popularity of content recommendation applications, multimodal recommendation has become one of the most prominent tasks in the research community. To promote breakthroughs in this field, we organize a Multimodal Click-through Rate prediction (MM-CTR) Challenge at the WWW 2025 EReL@MIR workshop. To meet the low-latency requirements of online inference in industrial applications, we have divided the MM-CTR Challenge into two sub-tasks: Multimodal Item Embedding and Multimodal CTR Prediction. The first task centers on developing multimodal item representation learning tailored for recommendation tasks, while the second focuses on designing CTR prediction models that effectively utilize multimodal embedding features to enhance model performance. Through in-depth exploration on these two tasks, we aim to broden the boundary of multimodal recommendation and call for solutions with practical value and insights for industrial recommender systems.
Please go to the challenge portal: https://www.codabench.org/competitions/5372/
We use the MicroLens-1M dataset released by Westlake University [1] for the MM-CTR Challenge. This dataset contains 1M users and 91K items, with detailed item content features (e.g., titles, covers). This challenge will use public data for training and private data for testing, respectively.
Dataset download: https://recsys.westlake.edu.cn/MicroLens_1M_MMCTR/
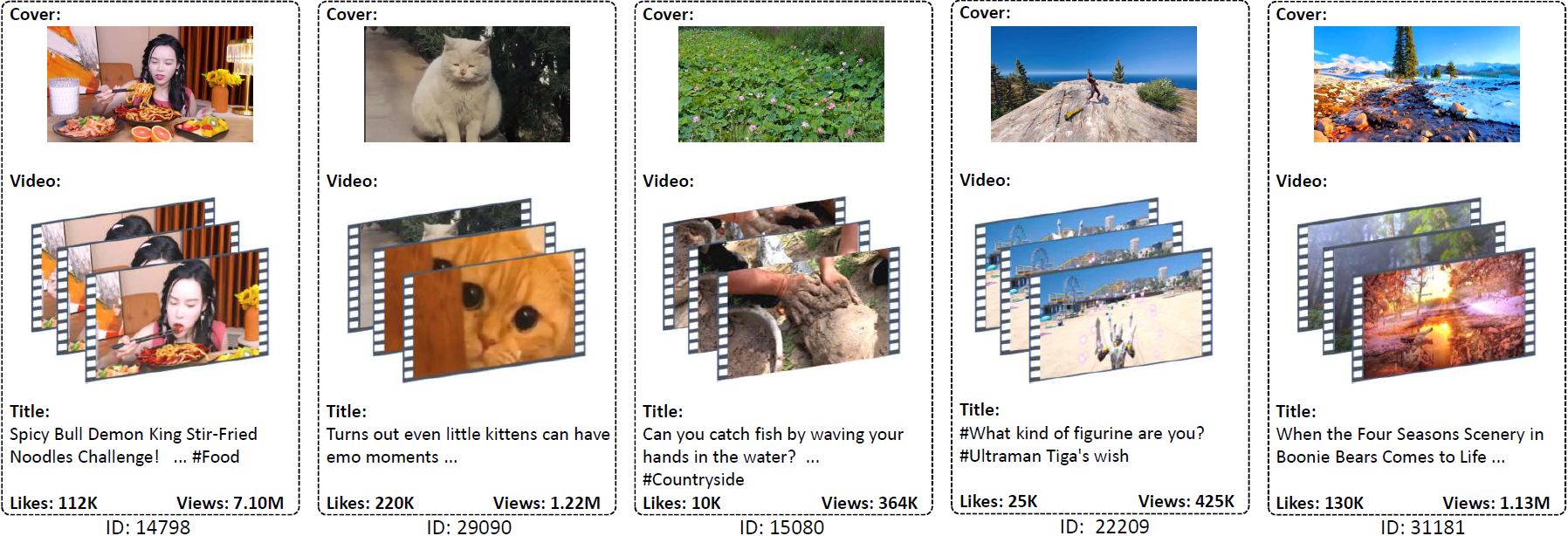
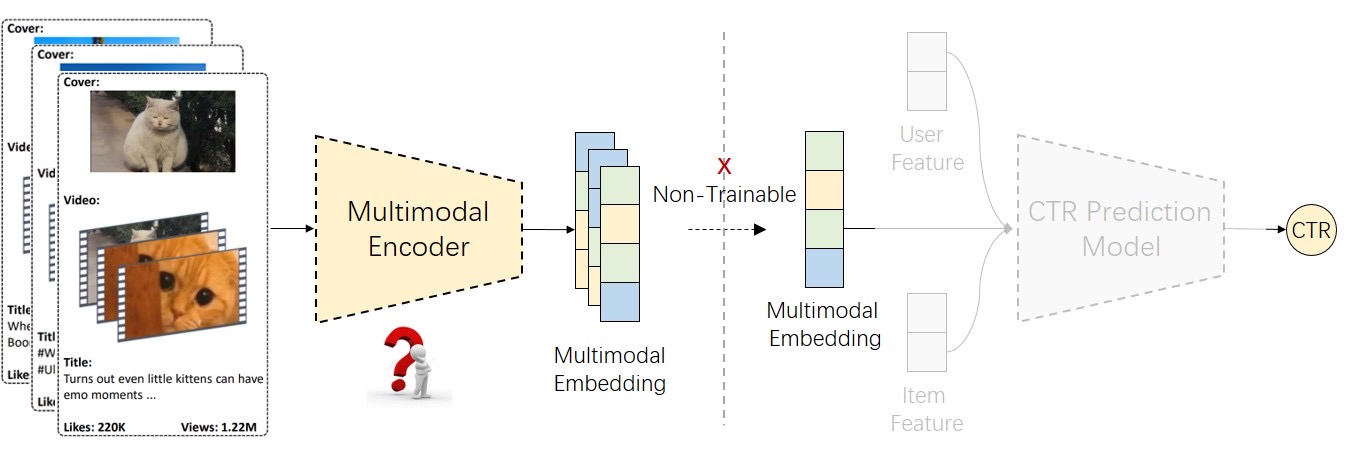
This challenge aims to explore multimodal information extraction and item representation learning methods that enhance recommendation tasks. The organizers will provide a fixed downstream CTR model to evaluate the effectiveness of item embeddings. Participants are free to use open-source multimodal models, and design algorithms to extract multimodal embeddings. Extracted embeddings must be saved in a specified format and combined with other ID features as input for downstream CTR model evaluation.
Task Input:
Task Output:
Participants are required to use the provided CTR model to evaluate the effectiveness of the multimodal embeddings. Specifically, they should replace the embedding features in the CTR model’s input with the features extracted in Task 1, retrain the model, evaluate its performance on the validation set, and predict pCTR on the test set for submission. In the preliminary round, participants only need to submit the pCTR prediction results. In the final round, participants must also submit reproducible training and inference code to extract multimodal embeddings. The final leaderboard will be ranked based on reproducible submission results. The evaluation metric is AUC.
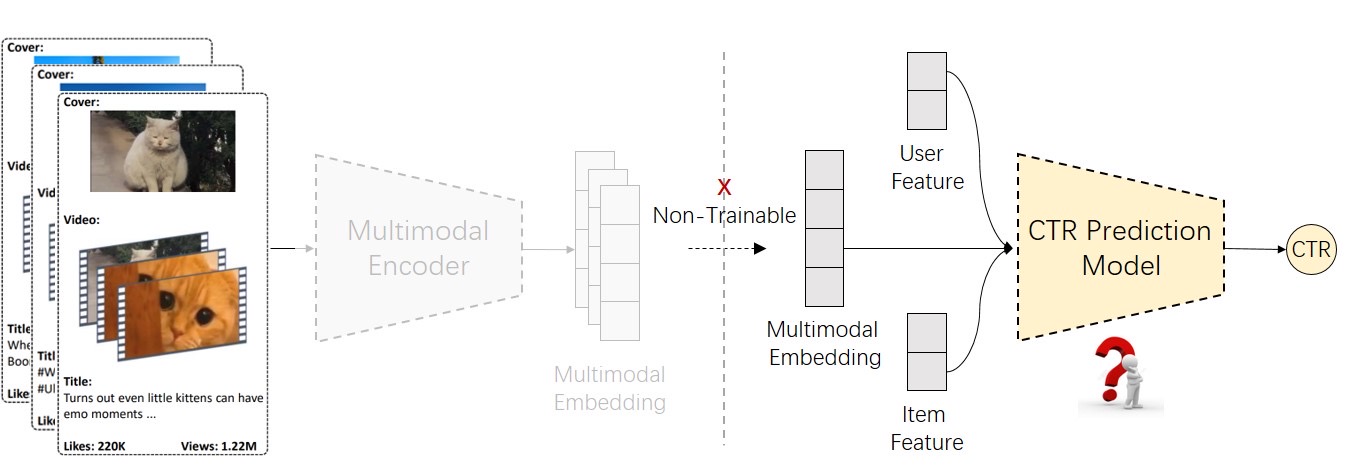
This task aims to explore what multimodal recommendation model can effectively leverage multimodal embedding features and achieve better performance. The organizers will provide extracted multimodal embeddings (from Task 1) and split user click data. Participants can improve the multimodal recommendation model based on the provided baseline model to enhance the CTR prediction results. Finally, participants will submit the predicted pCTR on the test set for competition.
Task Input:
Task Output:
Participants are required to use the multimodal embeddings provided by the organizers to evaluate the performance of the proposed CTR model. Specifically, they should replace the provided basedline model with the customized CTR model designed in Task 2, train the model, evaluate its performance on the validation set, and predict pCTR on the test set for submission. In the preliminary round, participants only need to submit the pCTR prediction results. In the final round, participants must also submit reproducible training and inference code for evaluation. The final leaderboard will be ranked based on reproducible submission results. The evaluation metric is AUC.
Using pretrained large models directly for CTR prediction is not allowed, but they can be used for item embedding extraction in Task 1.
The designed CTR model must be trained in an end-to-end manner, with the given features and on the given data split.
For practical considerations, only a single model using neural network are allowed. Ensemble methods or tree models are not allowed for training or testing.
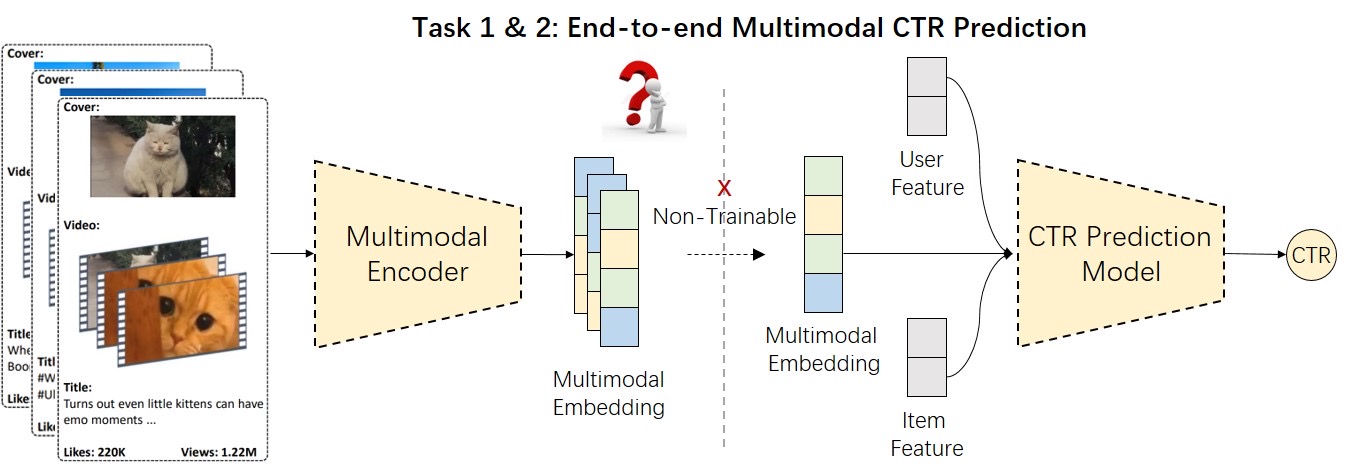
In this task, participants can optimize both tasks to enhance prediction accuracy. But instead of joint training of both tasks, which is impractical in production, we encourage partipicants to optimized embedding and CTR prediction models in a cascaded way. As a result, you need to build two seperate, disjoint models for multimodal item embedding and CTR prediction, where the former produce item embedding features and the latter optimizes the modeling of item embedding features. Both models can use the same model structure or different ones according to your choice, but the training should be performed separately.
Participants can choose one of the submission types listed below to engage in the challenge. We encourage participants to take on both challenges (Task 1 & 2) to fully enhance the pipepline of multimodal recommendation tasks and design better solutions.
Task 1 only: In this setting, the CTR model is fixed, and the focus is on optimizing the embeddings. Participants are not allowed to modify the model code used to evaluate the embeddings, but can adjust specified hyperparameters.
Task 2 only: In this setting, the embeddings are fixed, and the focus is on optimizing the CTR model. Participants are not allowed to change the input features, but can optimize the model structure and hyperparameters.
Task 1 & 2: In this setting, both the embeddings and the CTR model are optimized in a cascaded manner. Participants can modify both the embeddings and the CTR model, but no additional features are allowed. Two separate, disjoint models are required for Task 1 and 2 accordinly.
The challenge organizers will reproduce results based on the team’s submitted code and reproducibility guidelines, and the results will be publicly announced on the official website.
Task Submission Start: Jan. 26th, 2025
Code Submission Start: Mar. 7th, 2025
Final Submission End: Mar. 15th, 2025
Awarded Teams Release: Mar. 18th, 2025
Participants are required to submit their source code for model reproduction and final award competation. The review panel will reproduce results based on the leaderboard rankings, from highest to lowest. The top three teams in the reproduced results will be awarded as the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd place teams. Additionally, an Embedding Winner and a Model Winner will be selected for Task-1 and Task-2, respectively. If results cannot be reproduced or a team wins multiple awards, the prize will be passed to the next team.
Note that all rewards are pre-tax amounts and include applicable taxes.
The final winning teams must open-source their code under either the MIT License or the Apache License 2.0.
[1] Yongxin Ni, Yu Cheng, Xiangyan Liu, Junchen Fu, Youhua Li, Xiangnan He, Yongfeng Zhang, Fajie Yuan, A Content-Driven Micro-Video Recommendation Dataset at Scale, Arxiv 2023.